Frontiers Elevated Lactate by High-Intensity Interval Training Regulates the Hippocampal BDNF Expression and the Mitochondrial Quality Control System
$ 32.50 · 4.7 (554) · In stock
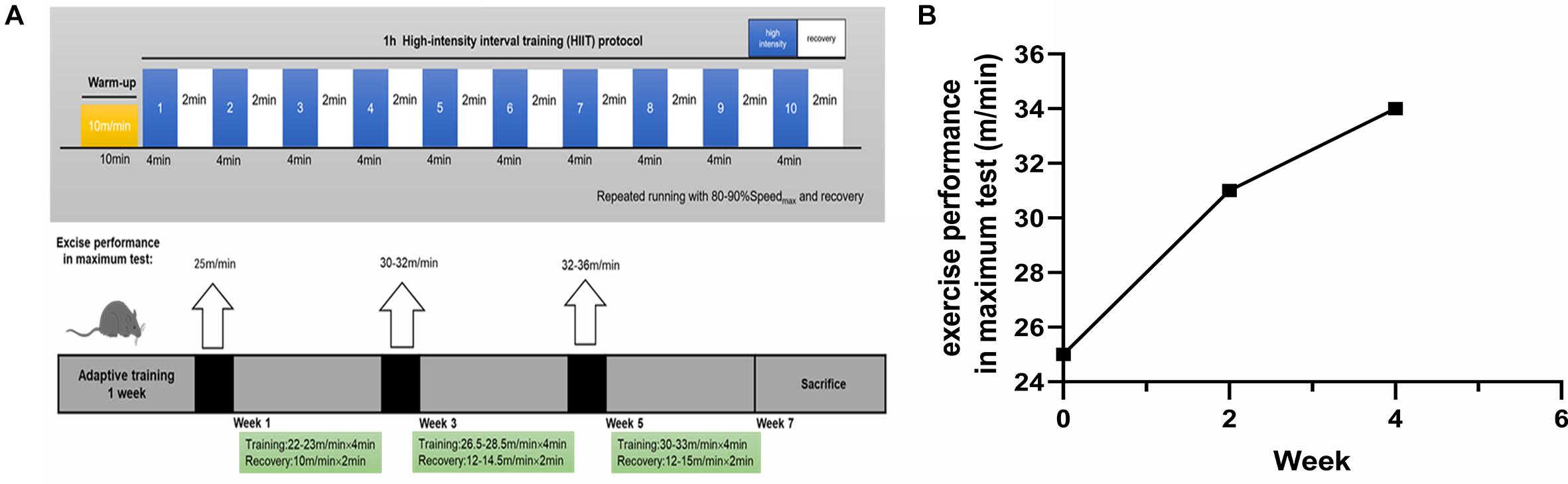

Figure 3 from Acute exercise increases brain region-specific expression of MCT1, MCT2, MCT4, GLUT1, and COX IV proteins.

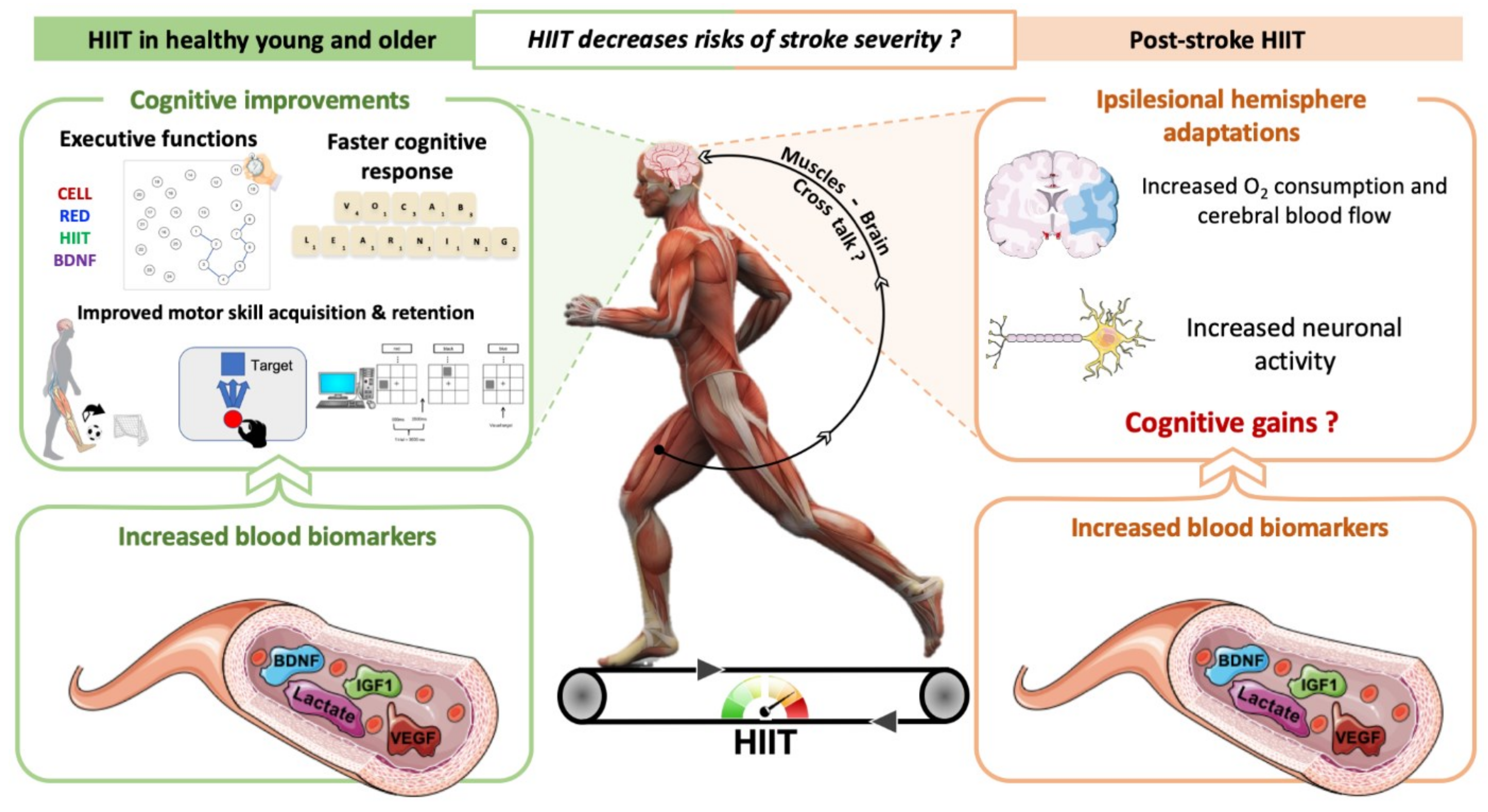
The potential mechanisms of lactate in mediating exercise-enhanced cognitive function: a dual role as an energy supply substrate and a signaling molecule, Nutrition & Metabolism
IJMS, Free Full-Text
PDF) L-Lactate Promotes Adult Hippocampal NeurogenesisData_Sheet_1.docxImage_1.TIFFImage_2.TIFFImage_3.TIFFImage_4.TIFFImage_5.TIFFImage_6.TIFF

Quality control system - List of Frontiers' open access articles
Frontiers Acute effects of two different work-to-rest ratio of high-intensity interval training on brain-derived neurotrophic factor in untrained young men

Mechanism proposed about the High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
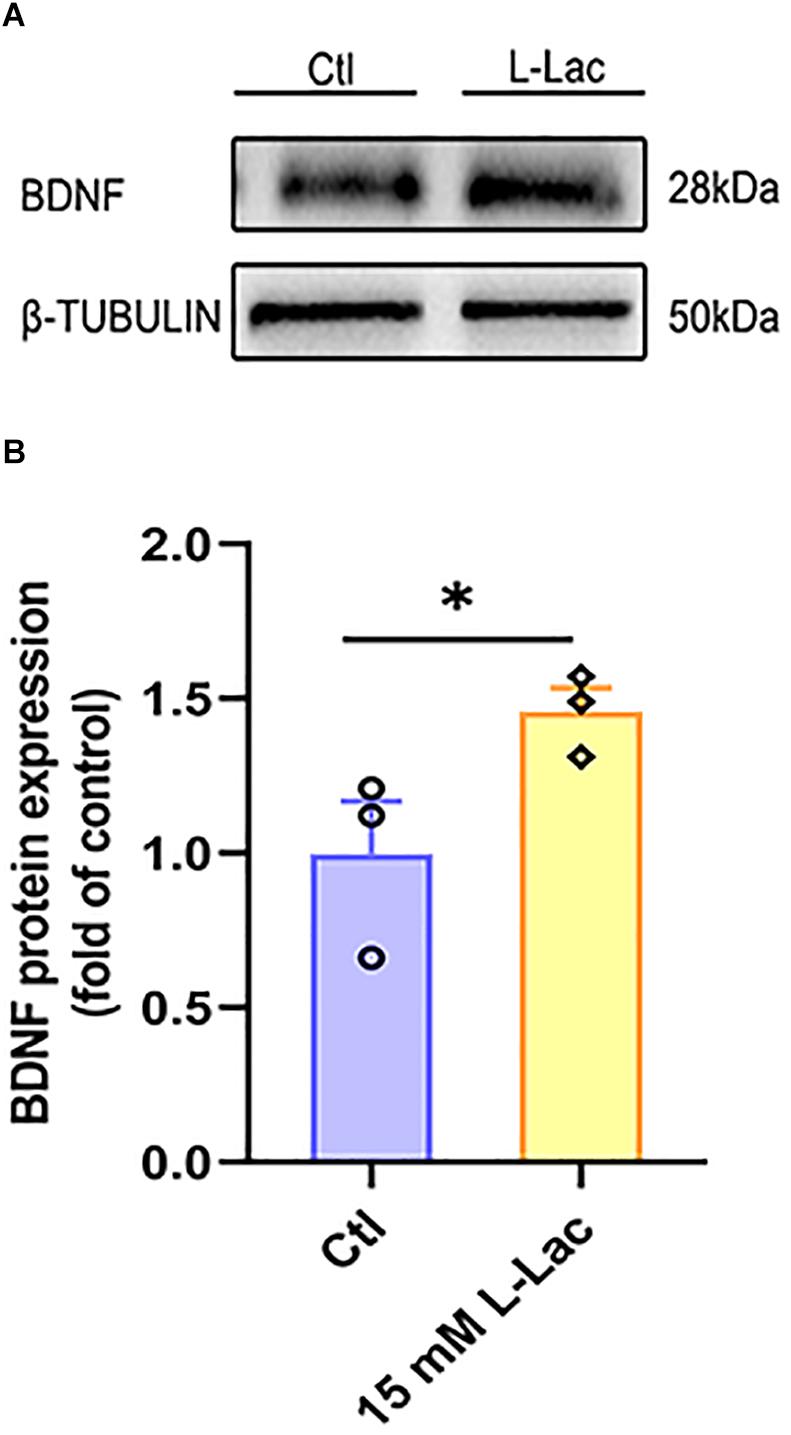
Frontiers Elevated Lactate by High-Intensity Interval Training Regulates the Hippocampal BDNF Expression and the Mitochondrial Quality Control System

Lactate Mediates High-Intensity Interval Training—Induced Promotion of Hippocampal Mitochondrial Function through the GPR81-ERK1/2 Pathway

Antioxidants, Free Full-Text

Antioxidants, Free Full-Text

High-intensity interval training is superior to moderate intensity training on aerobic capacity in rats: Impact on hippocampal plasticity markers - ScienceDirect

PDF) Exogenous L-lactate administration in rat hippocampus increases expression of key regulators of mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant defense
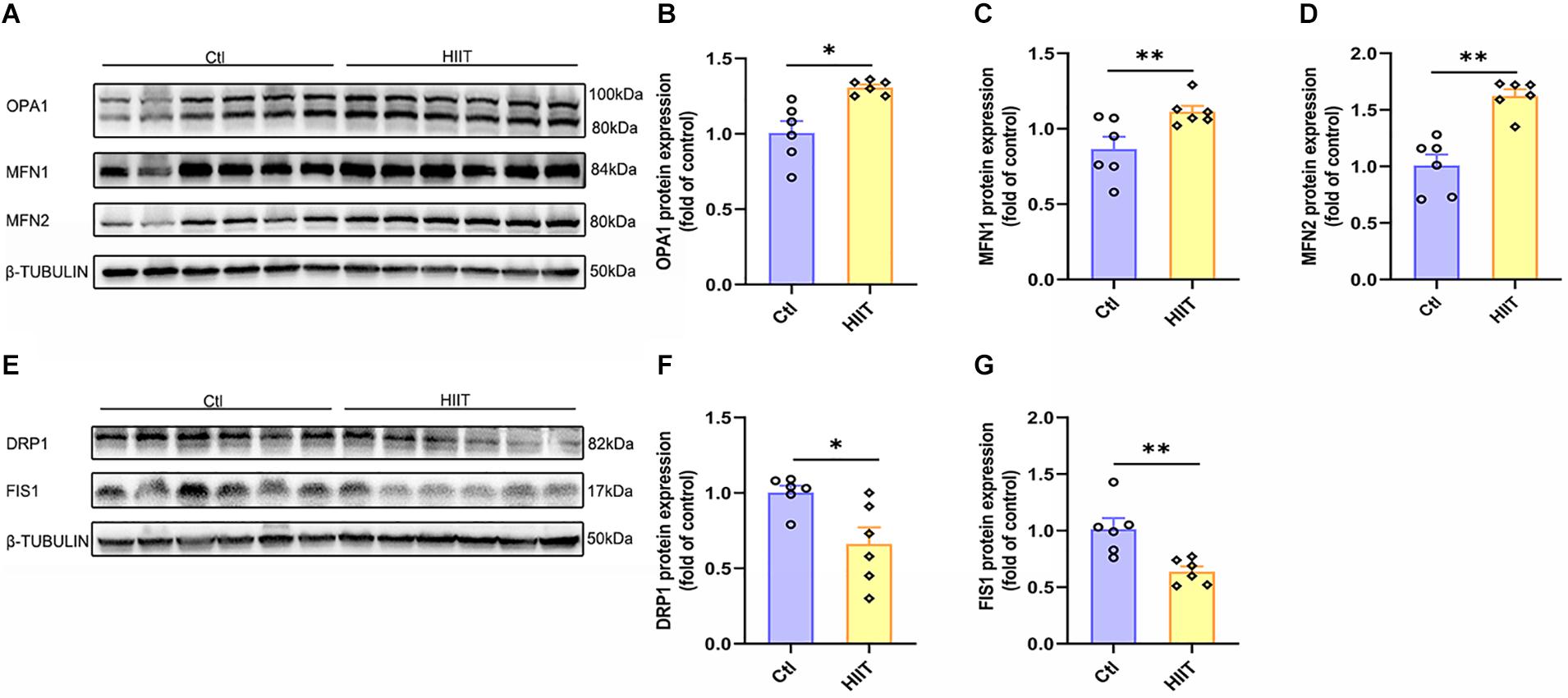
Frontiers Elevated Lactate by High-Intensity Interval Training Regulates the Hippocampal BDNF Expression and the Mitochondrial Quality Control System