Minerals, Free Full-Text
$ 13.99 · 4.5 (680) · In stock
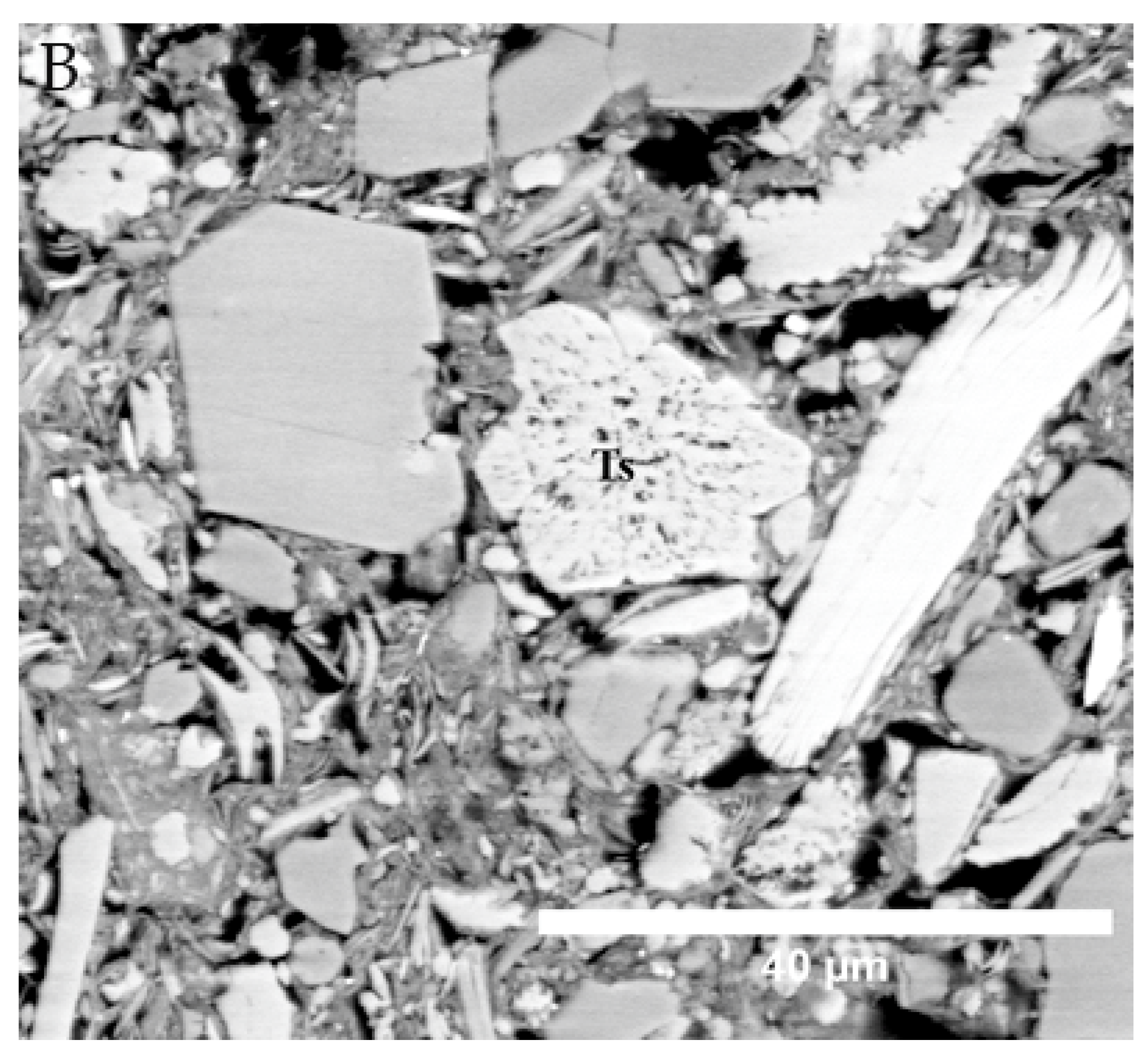
Distinguishing among deep-water sedimentary facies has been a difficult task. This is possibly due to the process continuum in deep water, in which sediments occur in complex associations. The lack of definite sedimentological features among the different facies between hemipelagites and contourites presented a great challenge. In this study, we present detailed mudrock characteristics of the three main deep-water facies based on sedimentological characteristics, laser diffraction granulometry, high-resolution, large area scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the synchrotron X-ray diffraction technique. Our results show that the deep-water microstructure is mainly process controlled, and that the controlling factor on their grain size is much more complex than previously envisaged. Retarding current velocity, as well as the lower carrying capacity of the current, has an impact on the mean size and sorting for the contourite and turbidite facies, whereas hemipelagite grain size is impacted by the natural heterogeneity of the system caused by bioturbation. Based on the microfabric analysis, there is a disparate pattern observed among the sedimentary facies; turbidites are generally bedding parallel due to strong currents resulting in shear flow, contourites are random to semi-random as they are impacted by a weak current, while hemipelagites are random to oblique since they are impacted by bioturbation.

Trace Minerals Enhanced Complex - Complete with 70+ Nutrient-Dense

Full Spectrum Minerals Capsules - Now Foods Canada

Minerals, Free Full-Text
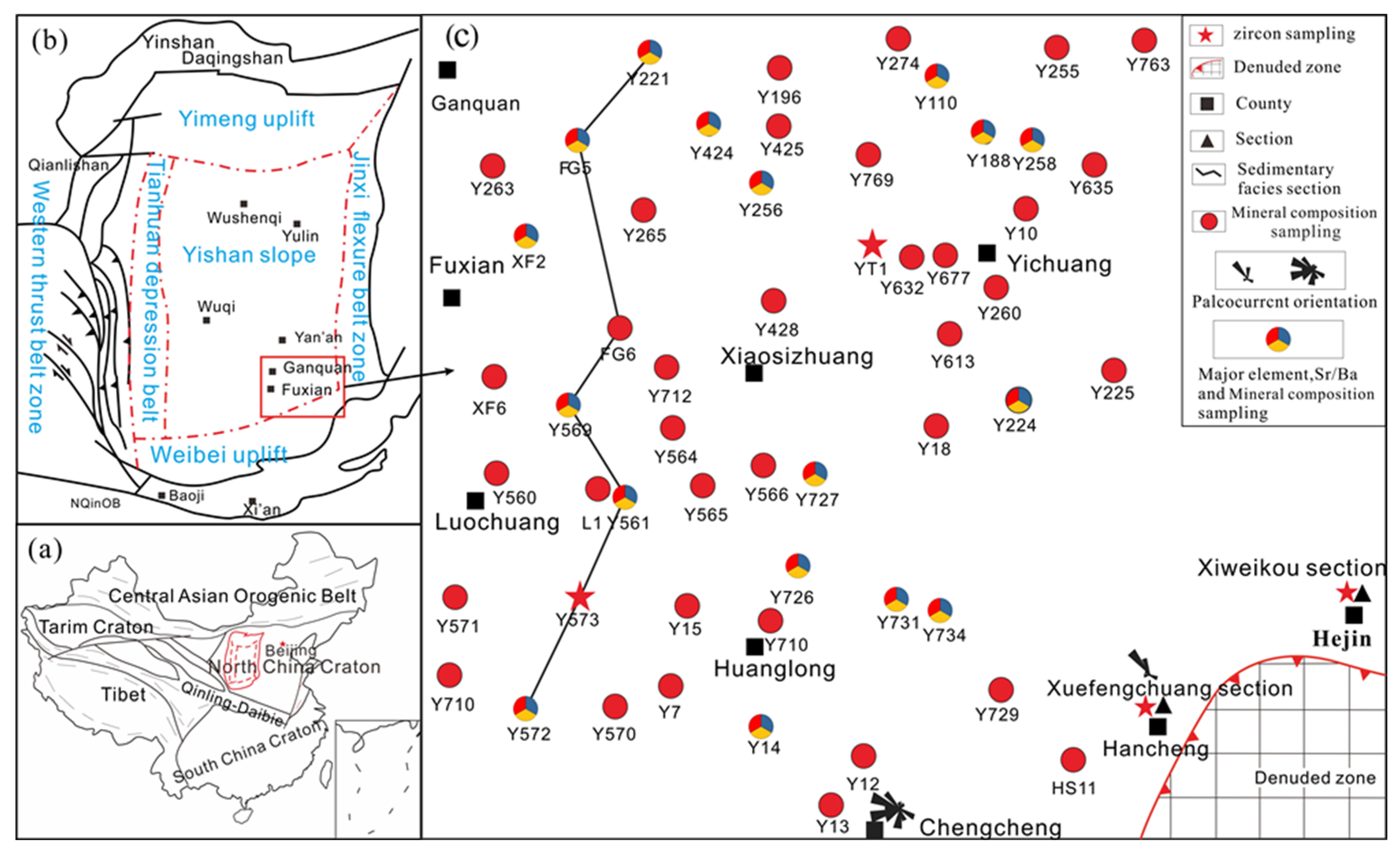
Minerals, Free Full-Text

allergen-free all-purpose flour S.M.A.R.T. Blend

Rocks and minerals - British Geological Survey
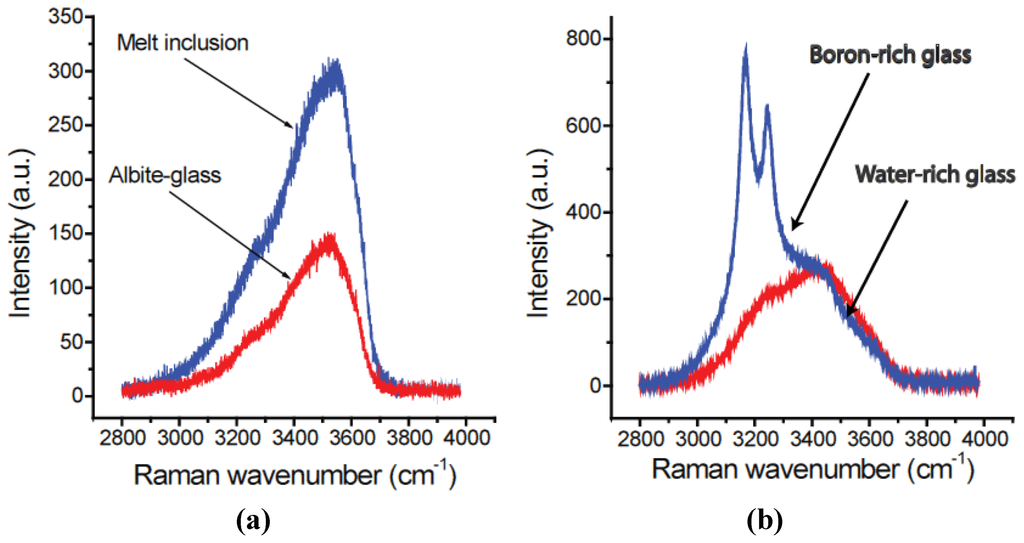
Minerals, Free Full-Text

What Minerals are in Drinking Water – Life Ionizers
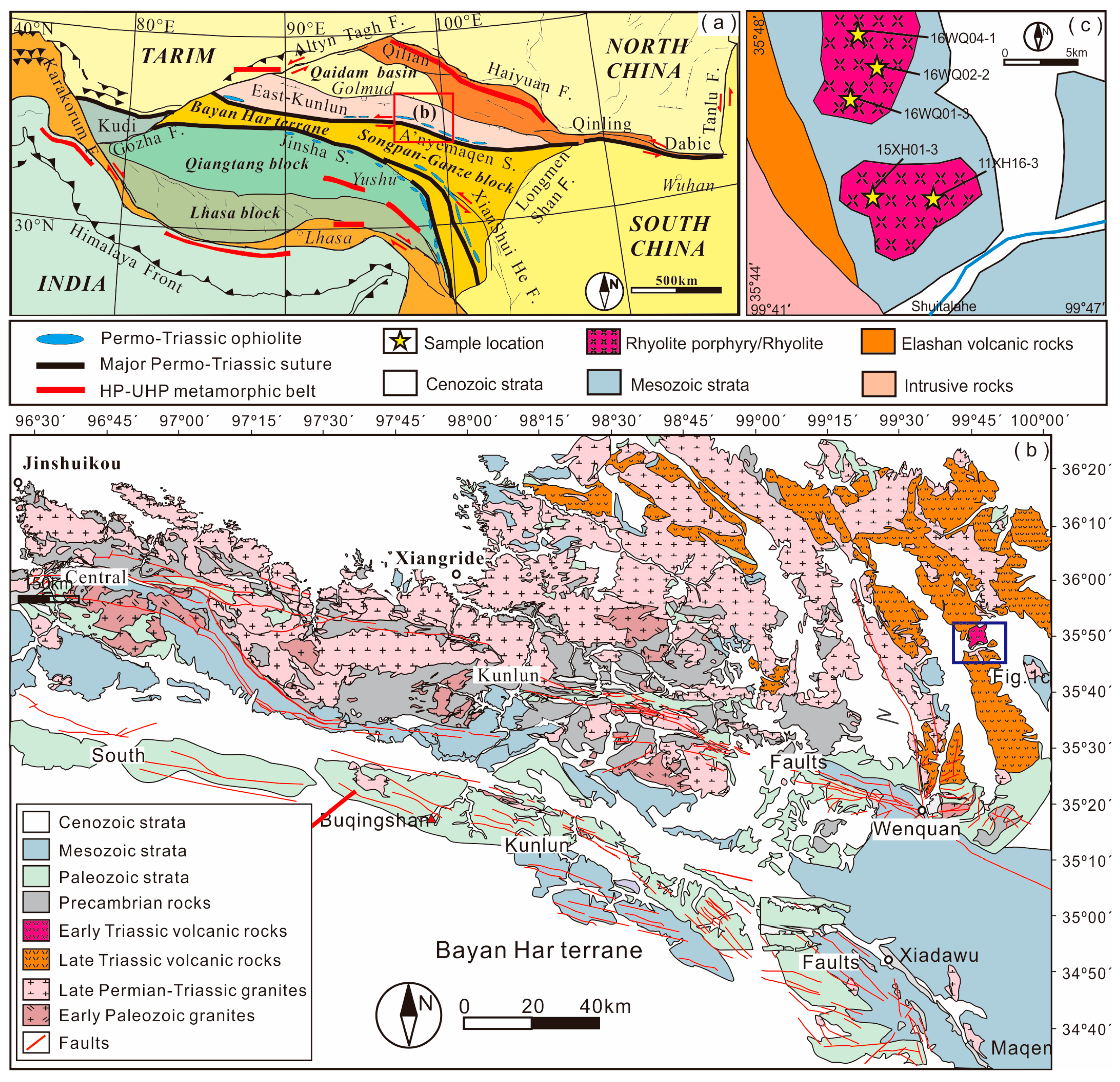
Minerals, Free Full-Text

Mineral, Types & Uses

Sun Star ConcenTrace Trace Mineral Drops

Minerals, Free Full-Text, mapa de islas king legacy

Minerals, Free Full-Text
Unique gems and minerals
