Effects of drought level (D), genotype (G), and their interaction on
$ 4.50 · 4.7 (552) · In stock

Download Table | Effects of drought level (D), genotype (G), and their interaction on leaf relative water content (RWC) and soluble sugars of sesame under three levels of drought (I 1 , I 2 , and I 3 = 55, 75, and 85% depletion of available soil water). from publication: Selecting Sesame Genotypes for Drought Tolerance Based on Some Physiochemical Traits | To assess drought tolerance, an understanding of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) physiological properties is needed. The objective of this study was to determine the physiological responses of sesame accessions to drought stress. The experiment was conducted as a two-way | Sesamum, Drought and Tolerance | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Integrated Microbiome and Metabolomic Analysis Reveal Responses of Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities and Root exudate Composition to Drought and Genotype in Rice (Oryza sativa L.), Rice

Gene-environment interactions across development: Exploring DRD2 genotype and prenatal smoking effects on self-regulation.

Exploring mechanisms of drought-tolerance and adaptation of selected sesame mutant lines - ScienceDirect

Recombinant Human EGF Protein, CF 236-EG-200: R&D Systems
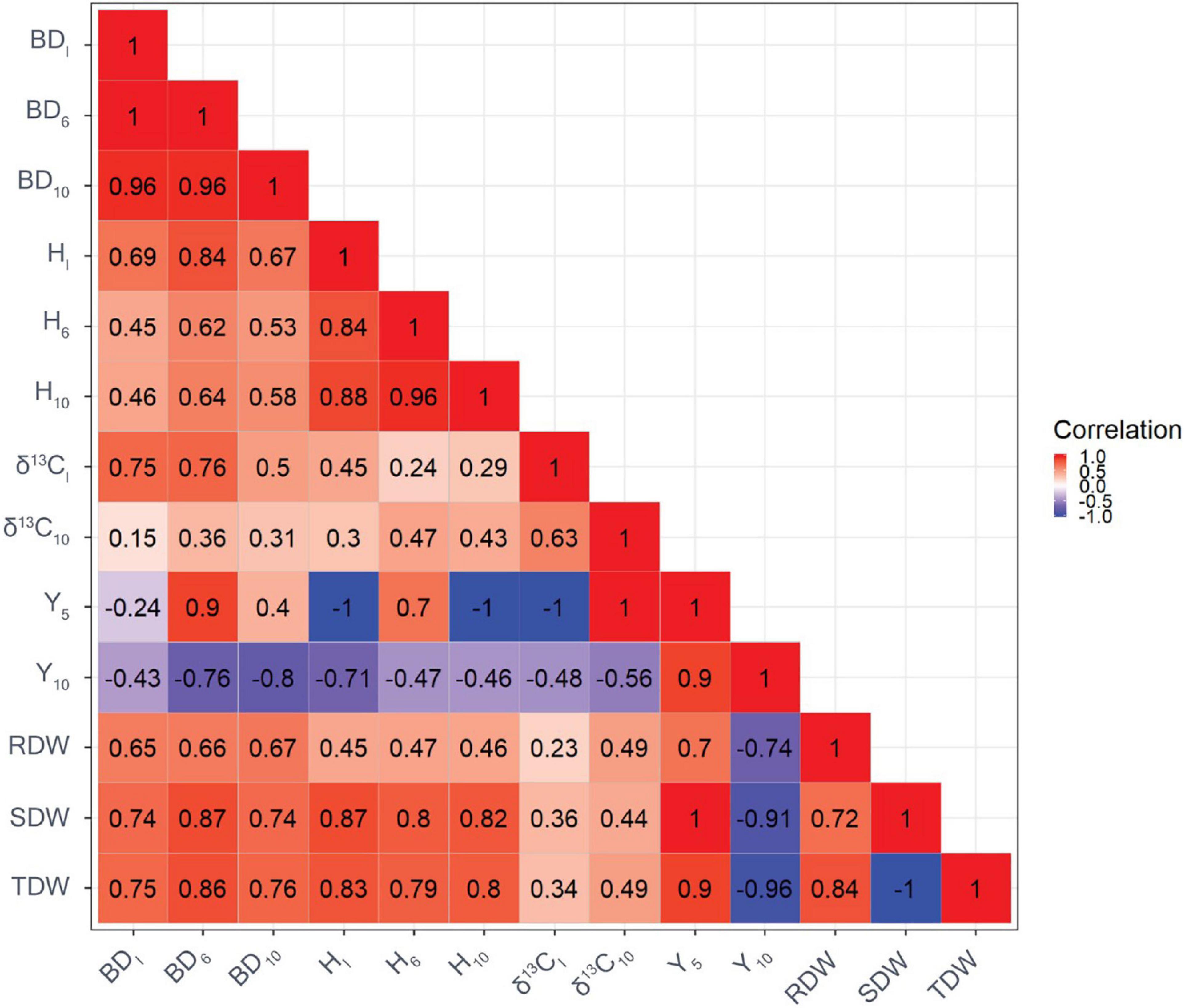
Frontiers Genetic Variation in Drought-Tolerance Traits and Their Relationships to Growth in Pinus radiata D. Don Under Water Stress

PDF) Selecting Sesame Genotypes for Drought Tolerance Based on Some Physiochemical Traits

Types of Drought: Cascading Effects

Crop Development – Shallot

Jamshid RAZMJOO, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan, IUT, Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding

Growth, Yield and Quality of Maize under Ozone and Carbon Dioxide Interaction in North West India - Aerosol and Air Quality Research

Better understand the interactions between DNA, RNA, and protein by using Illumina NGS for multiomic analysis

12: The Impact of Genetic Drift on Selected Alleles - Biology LibreTexts

Effects of drought level (D), genotype (G), and their interaction on