Influence of intentional femoral component flexion in navigated
$ 15.50 · 4.8 (153) · In stock

Referencing the center of the femoral head during robotic or computer- navigated primary total knee arthroplasty results in less femoral component flexion than the traditional intramedullary axis - ScienceDirect

Comparison of cementless twin-peg, cemented twin-peg and cemented single-peg femoral component migration after medial unicompartmental knee replacement: a 5-year randomized RSA study

Team - Clinica Adler

A Three-dimensional Comparison of Pre- and Post-component Position in a Series of Off-label Robotic-assisted Revision Total Knee Arthroplasties - ScienceDirect
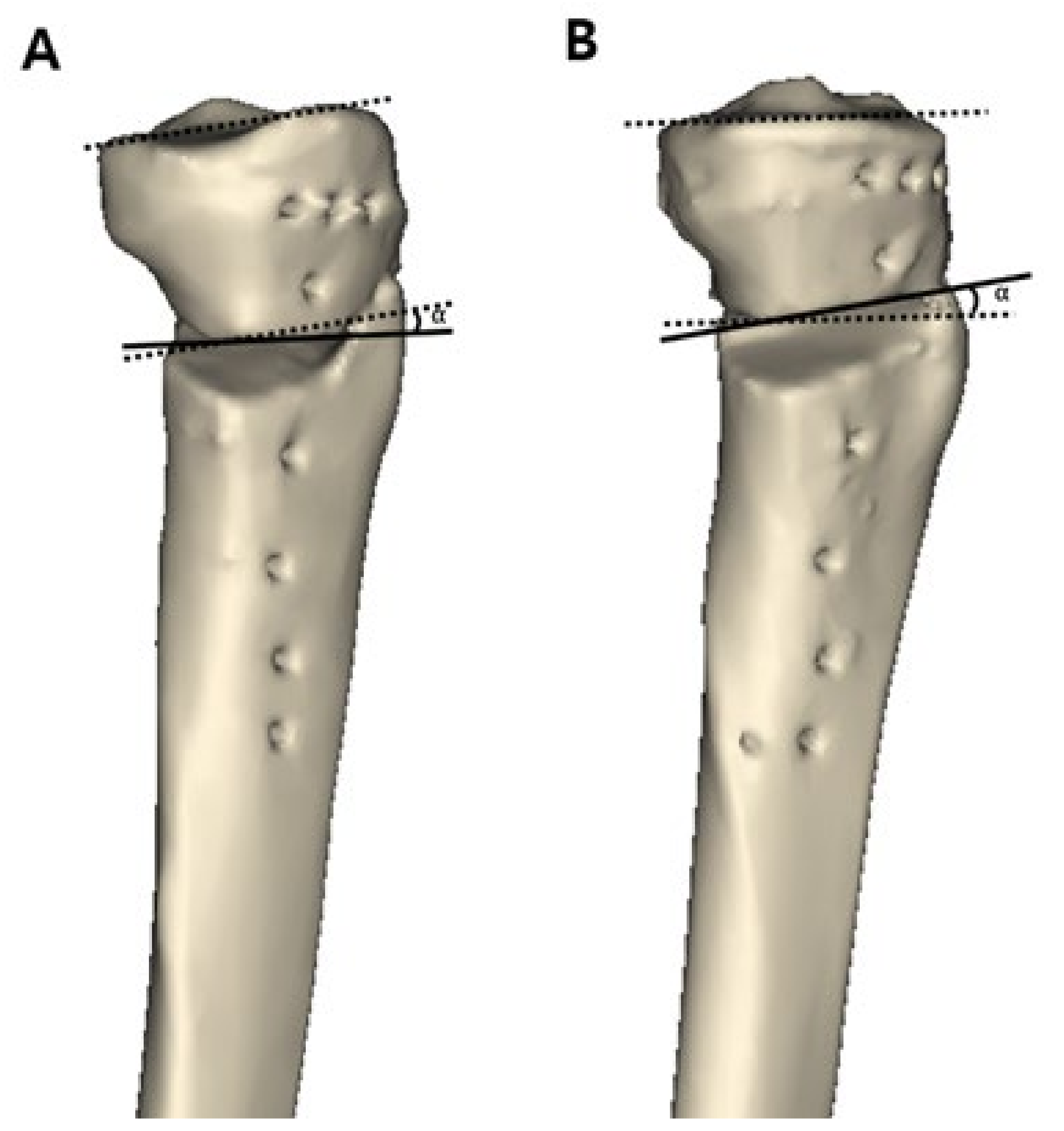
Appropriate determination of the surgical transepicondylar axis
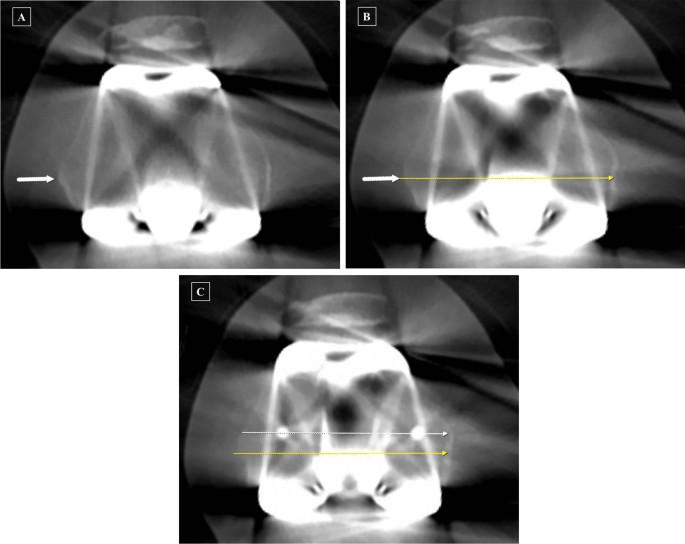
JCM, Free Full-Text
Alignment Targets in Total Knee Arthroplasty

Frontiers Prediction of knee biomechanics with different tibial component malrotations after total knee arthroplasty: conventional machine learning vs. deep learning

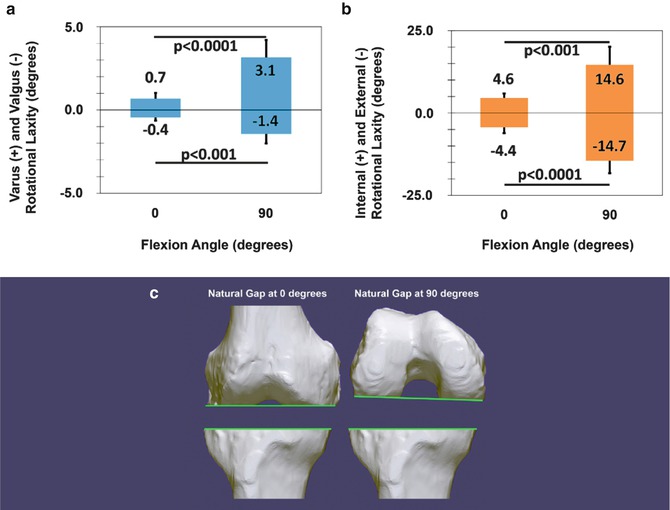
Dynamic knee behaviour: does the knee deformity change as it is flexed—an assessment and classification with computer navigation

Internal femoral component rotation adversely influences load

Does mild flexion of the femoral prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty result in better early postoperative outcomes?, BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders

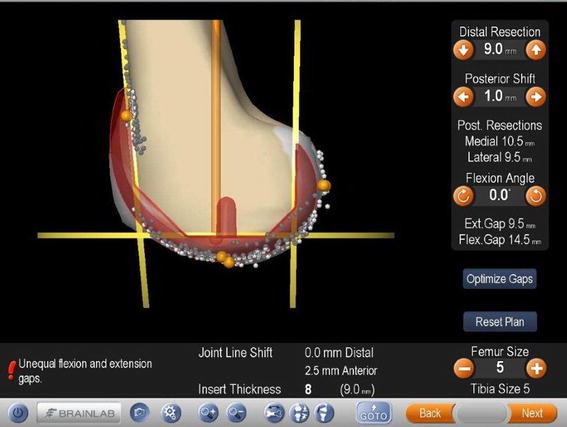
Ligament balancing support. The ligamentous tension, the axis of the